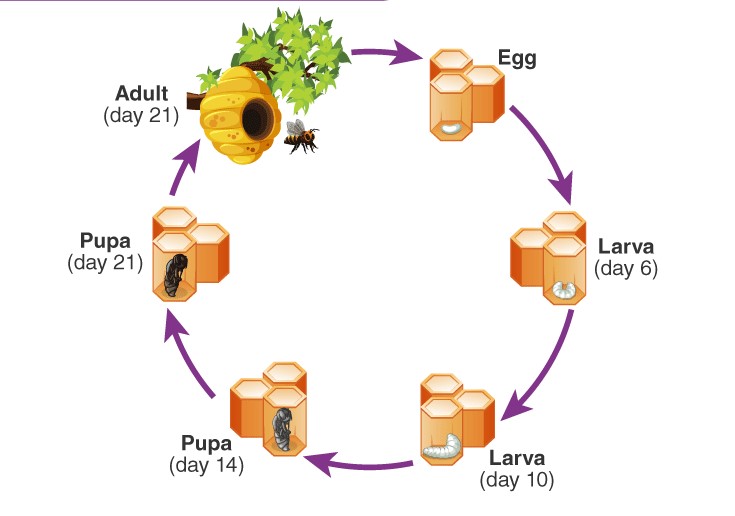

Honey bees play a crucial role in pollination, supporting biodiversity and agriculture. Understanding their lifespan is essential for beekeepers and nature enthusiasts. The lifespan of a honey bee depends on its role in the colony, environmental factors, and seasonal changes. In this detailed guide, we will explore how long honey bees live and the factors that influence their longevity.
1. The Lifespan of a Worker Bee Worker bees, the female bees responsible for various tasks in the hive, have different lifespans depending on the season. In the summer, worker bees live between 4 to 6 weeks due to their exhausting workload of foraging, nursing, and hive maintenance. However, in winter, worker bees can live up to 4 to 6 months as they conserve energy and focus on keeping the colony warm.
2. The Lifespan of a Queen Bee The queen bee has the longest lifespan among all members of the hive. On average, a healthy queen bee can live between 2 to 5 years. Her longevity depends on genetics, environmental conditions, and the colony’s health. Beekeepers often replace queens after a few years to maintain strong hive productivity.
3. The Lifespan of Drone Bees Drones, the male bees in a colony, have the shortest lifespan. They usually live between 1 to 2 months. Their primary role is to mate with a queen from another colony. After mating, they die immediately. If they fail to mate, worker bees may expel them from the hive before winter to conserve resources.
4. Factors That Affect Honey Bee Lifespan Several factors influence how long honey bees live. These include:
- Seasonal Changes: Worker bees live longer in winter compared to summer.
- Nutrition: Access to diverse and nutrient-rich pollen sources extends their lifespan.
- Pesticides and Chemicals: Exposure to harmful pesticides can shorten their lives.
- Diseases and Parasites: Varroa mites and bacterial infections can significantly reduce their lifespan.
- Colony Stress: Environmental stressors, such as habitat loss and climate change, impact their survival.
5. Why Do Summer and Winter Worker Bees Have Different Lifespans? The difference in lifespan between summer and winter worker bees is mainly due to their roles. Summer bees work tirelessly collecting nectar and pollen, which wears out their bodies quickly. Winter bees, however, store energy and rarely leave the hive, which helps them live longer.
6. How Beekeepers Can Help Prolong Honey Bee Lifespan Beekeepers play an essential role in extending the lifespan of honey bees by:
- Providing supplemental feeding during scarcity.
- Reducing exposure to harmful pesticides.
- Treating hives for diseases and pests.
- Ensuring proper ventilation and hive management.
7. The Importance of Honey Bee Lifespan in Pollination A healthy bee population ensures effective pollination of crops and wild plants. Since worker bees have a short lifespan, continuous reproduction is crucial for maintaining a strong colony. Understanding their life cycle helps beekeepers and farmers support pollination efforts.
Understanding Honey Bee Longevity The lifespan of honey bees varies depending on their role in the hive. Worker bees live for weeks or months, drones for a couple of months, and queens for several years. Environmental factors, diseases, and hive conditions all contribute to how long honey bees live. By taking steps to protect them, we can ensure they continue to thrive and support our ecosystem.
